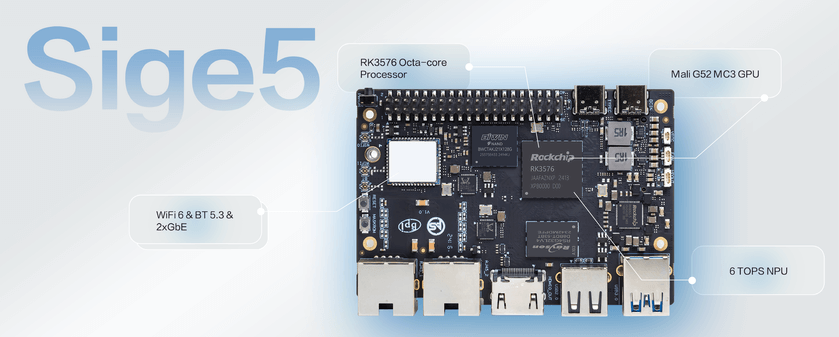
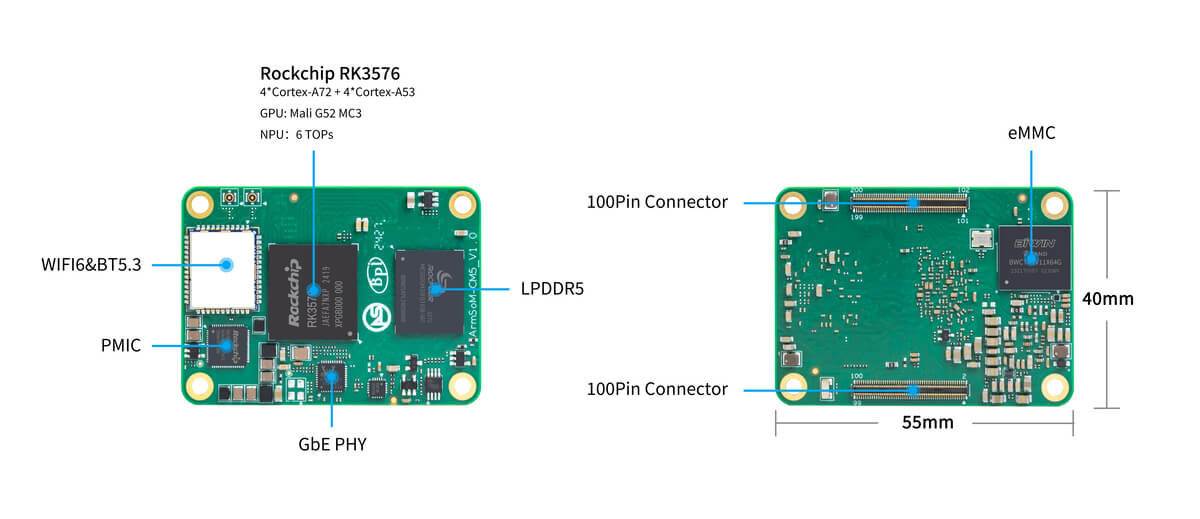
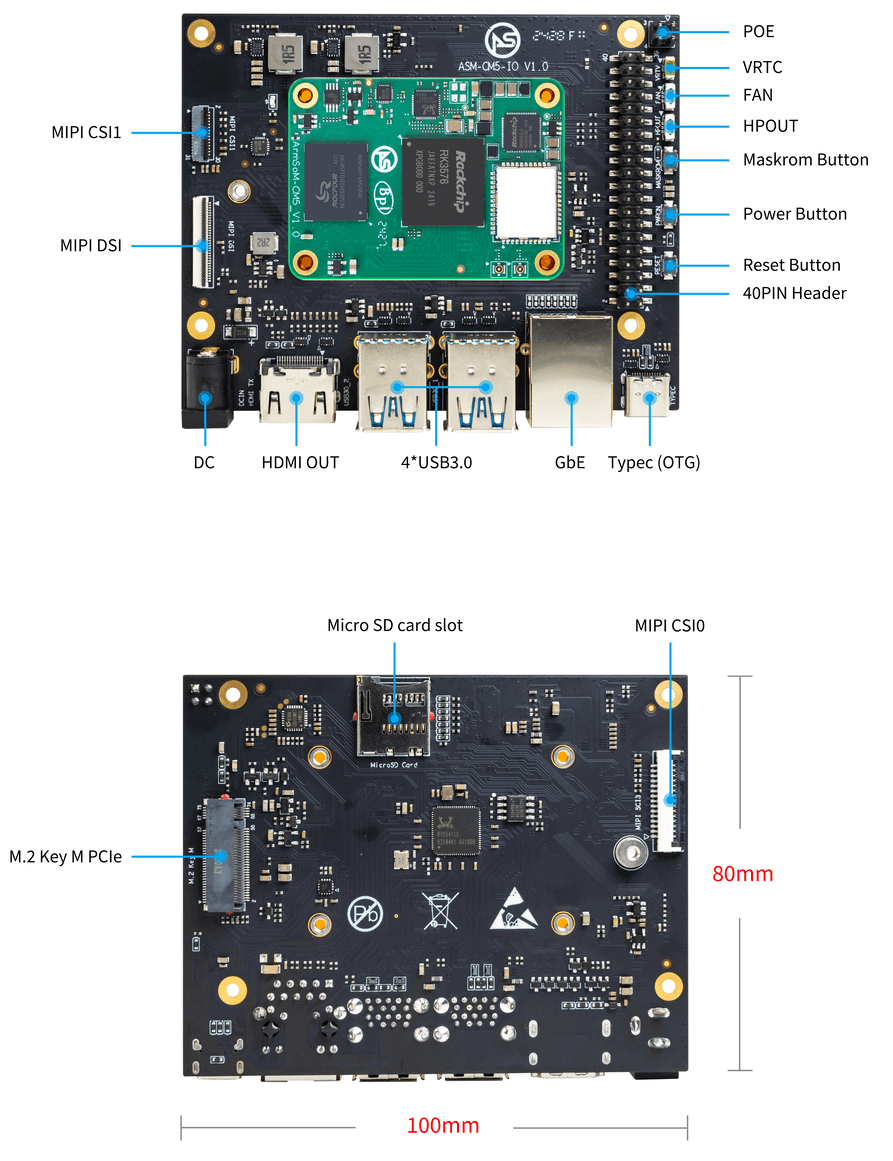
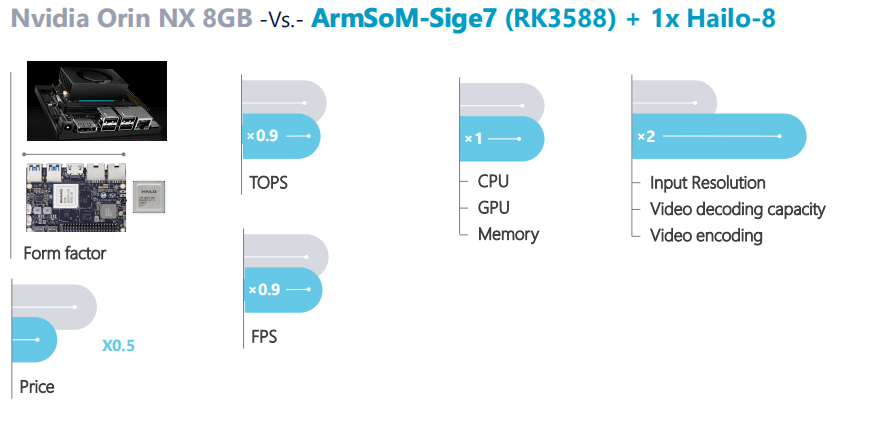
In modern intelligent hardware development, choosing a development board with stable performance and low power consumption is key to ensuring product success. The latest RK3506 chip from Rockchip, with its excellent power efficiency, versatile expansion capabilities, and outstanding real-time performance, has become a popular choice in fields such as smart home appliances, industrial control, and handheld terminals. The ArmSoM RK3506 development board, based on the RK3506 chip, provides developers with complete hardware resources and a convenient development platform, making it the preferred solution for many projects.
This article will detail the specifications, performance advantages, and wide application scenarios of the RK3506 development board, helping developers better understand how this development board drives innovation in intelligent hardware.
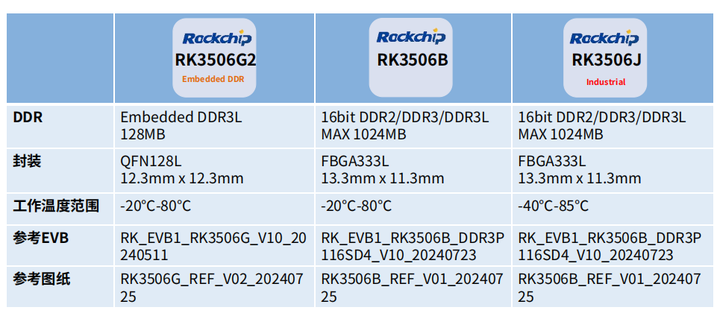
The RK3506 development board is equipped with a tri-core Cortex-A7 processor, with a frequency of up to 1.5GHz, supporting multi-tasking and efficient parallel processing. Additionally, the RK3506 features a 2D hardware acceleration engine that enhances graphics rendering and UI performance. It supports DDR2/DDR3/DDR3L memory, with a maximum expansion of 1GB, meeting the needs of most embedded devices.
Key Specifications of the RK3506 Development Board:
- CPU: Tri-core Cortex-A7, up to 1.5GHz
- Graphics Engine: 2D hardware acceleration
- Memory: Supports DDR2/DDR3/DDR3L, up to 1024MB
- Interfaces: Includes USB OTG, dual 100Mbps Ethernet ports, UART, SPI, etc.
- Audio and Video Capabilities: Supports 720P video decoding, integrates AEC, ANR, and other audio algorithms.
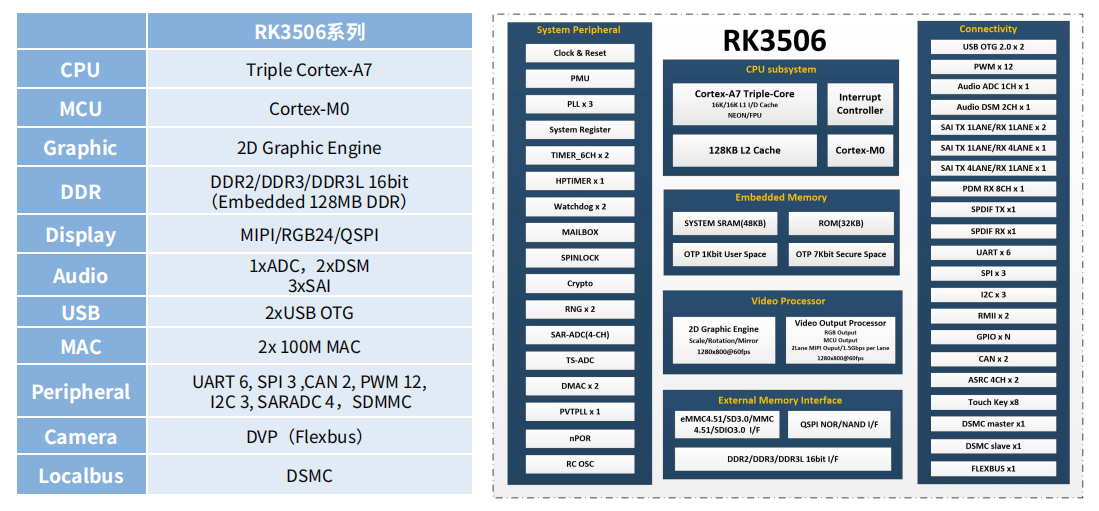
1.1 RK3506 Development Board Interface Features
The RK3506 development board provides various standard interfaces, including USB OTG, dual 100Mbps Ethernet ports, UART, SPI, etc., which meet the connection needs of various embedded applications. The rich interface options and expandability allow developers to design and customize solutions flexibly.
2. Versatility of the RK3506 Development Board Across Multiple Scenarios
The RK3506 development board features a dual processor architecture with a tri-core Cortex-A7 and a Cortex-M0 core, supporting RTOS, Linux, and other multi-system combinations. Its powerful multi-core performance and rich peripheral interfaces enable it to be widely applied in various fields:
- Smart Home Appliances: The RK3506 provides ultra-low power consumption and integrated voice algorithms, offering a smooth user experience and enhancing product intelligence.
- Industrial Control: In industrial gateways, the RK3506 development board supports dual 100Mbps Ethernet and various industrial protocols, helping industrial devices achieve interoperability.
- Handheld Terminals: With a power consumption of just 200mW, the RK3506 development board offers excellent portability and security for handheld POS devices, making it ideal for various commercial applications.
3. Display Product Advantages of the RK3506 Development Board
The RK3506 development board also shows its strength in display-related products. It supports the Linux SDK and RT-Thread 4.1 SMP multi-core processing, significantly improving thread concurrency and performance, making it suitable for real-time applications.
3.1 RK3506 Linux SDK Introduction
The RK3506 development board supports the official Linux SDK, allowing developers to quickly develop and optimize products, improving system responsiveness and stability.
3.2 RK3506 RT-Thread 4.1 SMP Support
The RK3506 development board supports RT-Thread 4.1 SMP symmetric multi-core processing, enabling load balancing and task core switching, significantly enhancing multi-tasking efficiency, ideal for real-time systems.
3.3 RK3506 Development Board’s Superior UI Rendering Capabilities
The RK3506 development board boasts strong graphical rendering capabilities, smoothly displaying complex UIs, making it an excellent choice for products such as smart homes and digital signage.
4. Control Product Advantages of the RK3506 Development Board
The RK3506 development board also excels in control-related applications. Its real-time performance and multi-system support make it an ideal choice for industrial automation.
4.1 RK3506 AMP Multi-System Solution
The RK3506 development board supports the AMP multi-system solution, allowing RTOS and Linux to run simultaneously on the same chip, meeting a variety of application needs.
4.2 RK3506 Development Board’s Strong Real-Time Performance
The RK3506 development board offers powerful real-time performance, ensuring quick system response to various input signals, especially for high-precision control systems.
| Chip Model | RK3506 (Binding Real - time Core not Participating in System Other Scheduling) | T1*3 (Binding Real - time Core not Participating in System Other Scheduling) | RK3506 (Closing an A7 Core, Binding Real - time Core not Participating in System Other Scheduling) | T1*3 (Not Binding Real - time Core not Participating in System Other Scheduling) |
|---|
| CPU | 2*Cortex - A7 | 2*Cortex - A7 | 3*Cortex - A7 | 2*Cortex - A7 |
| CPU Frequency | 1200MHz | 1200MHz | 1300MHz | 1300MHz |
| DDR | 16bit DDR3 800MHz | 16bit DDR3 800MHz | 16bit DDR3 800MHz | 16bit DDR3 800MHz |
| L1 Cache | 32 KB I/D | 32 KB I/D | 16 KB I/D | 16 KB I/D |
| L2 Cache | 256 KB | 256 KB | 128 KB | 128 KB |
| Preempt - RT Latency | ≈70us | ≈102us | ≈62us | ≈62us |
| Xenomai Latency | ≈68us | ≈68us | | |
4.3 RK3506 Development Board’s EtherCAT Bus Optimization
The RK3506 development board is specifically optimized for the EtherCAT bus, supporting IgH and CODESYS protocols. By connecting multiple servo drive slaves via Ethernet, it achieves precise control of servo motors, with latency jitter performance below 10%, ensuring high-precision control.
5. ArmSoM RK3506 Development Board: Simplifying Development
The ArmSoM RK3506 development board, based on the RK3506 chip, provides developers with complete hardware resources, including schematic diagrams and PCB files, along with the official Linux SDK. The ArmSoM RK3506 development board also supports the lightweight UI framework LVGL and quick startup functionality, greatly simplifying the development process. Whether for intercom systems, handheld POS devices, or industrial gateways, developers can easily bring their ideas to life with the ArmSoM RK3506 development board.
Development Timeline: The RK3506 development board is expected to go into mass production in early 2025, offering efficient, intelligent solutions to more industries.
Conclusion
The RK3506 development board, with its high performance, low power consumption, and extensive expansion capabilities, has become the ideal choice for smart hardware, industrial control, and handheld terminal applications. Based on the RK3506 chip, the ArmSoM RK3506 development board provides a powerful and user-friendly hardware platform, helping developers quickly turn their ideas into products. Whether it's smart home appliances, industrial gateways, or handheld POS devices, the ArmSoM RK3506 development board offers a stable platform and comprehensive technical support, ensuring the success of intelligent hardware projects.