4. Start the system
When running the product for the first time, two steps are required: burning the system and starting the system
We have already explained how to burn the system. Now let’s explain how to start the system
Starting the system requires correctly connecting the storage device and performing power-on startup and other operations. For details, please refer to this article.
You can use serial port login or SSH to log in to the system. If we have connected a screen, we can directly enter the desktop system through the manager displayed on the display.
4.1 Product startup method
The ArmSoM series of products supports multiple startup methods. Our current products mainly use eMMC and SD card startup, and some product hardware supports NVME startup.
For products without onboard eMMC, only SD card startup is supported. When the system image is burned in the SD card, it will start from the SD card.
For products with onboard eMMC and TF card slot, both eMMC and SD card startup methods are supported.
SD card boot -> eMMC boot -> SD card and eMMC have no image, boot failed
4.2. Boot precautions
The Linux system image is burned on the eMMC or SD card, and the product will run automatically when powered on.
The following are the product startup precautions:
Connect the onboard peripherals correctly according to the product interface diagram, especially the devices that do not support hot plug (MIPI-CSI display, MIPI-DSI camera, PCIE-WIFI network card, PCIE-4G network card, SSD hard disk, etc.). If you plug and unplug the device when it is powered on, it may damage the device and make it unable to work properly.
When using the display, please note that the MIPI interface does not support hot plug. There are two forms of HDMI interface, one is the standard HDMI interface, and the other is micro-HDMI. The two interfaces cannot be directly connected, and an adapter is required to convert the connection. If it is a display with VGA, DP interface, it can also be displayed by using an adapter.
The product supports mouse and keyboard, and can be connected through the USB interface if necessary.
Use a power supply to power the product. Note: The power specifications marked in the product documentation are the specifications for normal use of the product. If there are many peripherals connected, please use a power supply with the same voltage and higher power.
The image will enter the Recovery mode to configure the product for the first start after burning. It will automatically restart after one or two minutes of power on. After restarting, the system will run normally
4.3 Login method
4.3.1 Serial terminal access
Our product defines the 6th (GND), 8th (TX), and 10th (RX) pins on the 40PIN GPIO pins as UART serial communication interfaces or have a separate Debug debugging interface to facilitate troubleshooting problems in the early startup stage of the system.
Connect the USB to TTL serial cable as shown below:
| ArmSoM product | Connection | Serial port module |
|---|---|---|
| GND (pin 6) | ---> | GND |
| TX (pin 8) | ---> | RX |
| RX (pin 10) | ---> | TX |
Serial port parameter configuration
The default serial port configuration of Rockchip-based ArmSoM products is as follows:
baudrate: 1500000
data bit: 8
stop bit: 1
parity : none
flow control: none
4.3.2 Using serial port debugging on Windows
Putty or SecureCRT is generally used on Windows. Among them, we recommend the free version of MobaXterm. This is a powerful terminal software. Here we introduce it. The usage of MobaXterm is similar to it.
Download MobaXterm here:
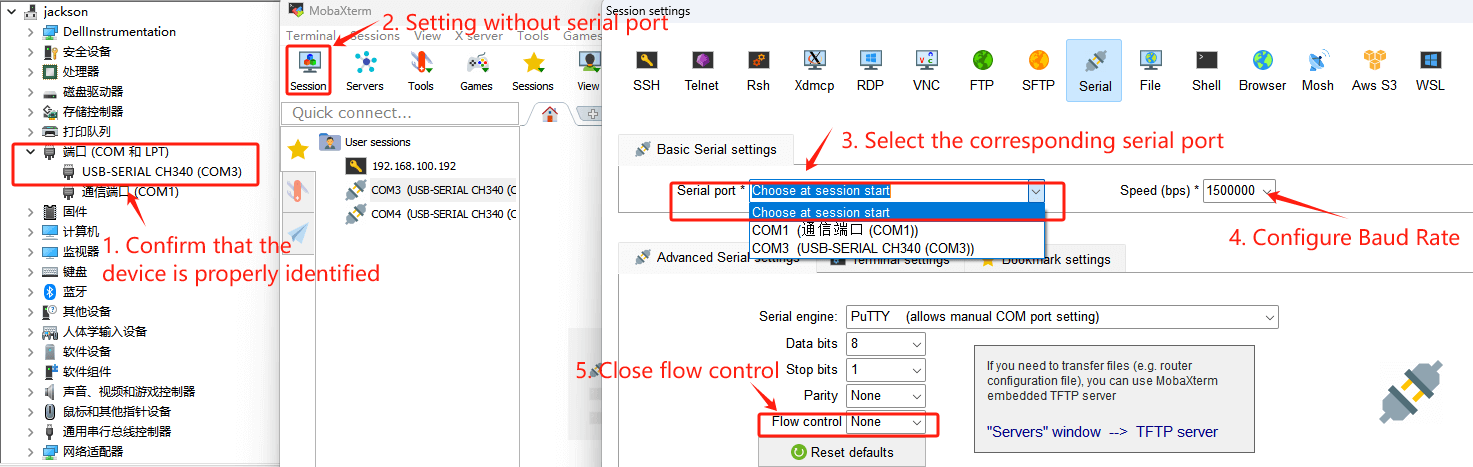
Connect the serial port module with a computer, then open the computer's device manager and check the port name
1. Select session as Serial.
2. Change Serial port to the COM port found in the device manager.
3. Set Speed (bsp) to 1500000.
4. Click the OK button.
4.3.3 Using serial port debugging on Linux
There are many options on Linux:
- minicom
- picocom
- kermit
The following is an introduction to the use of minicom. For other software, refer to the online software usage
4.3.3.1 Install minicom
sudo apt-get install minicom
After connecting the serial cable, check what the serial device file is. The following example is /dev/ttyUSB0
# ls /dev/ttyUSB*
/dev/ttyUSB0
The serial port has no permission to read. Temporary solution: Use chmod command
sudo chmod 777 /dev/ttyUSB0
Permanent solution: Add the current user to the dialout group
sudo usermod -aG dialout current username
4.3.3.2 Set minicom
- Edit ~/.bashrc, add the following parameters, and reopen a new terminal to take effect.
alias minicom='minicom -w -t xterm -l -R UTF-8'
- Create and edit the file ~/.minirc.rockchip, add the following content, the purpose of this is to set the configuration of rockchip.
pu port /dev/ttyUSB0
pu baudrate 1500000
pu bits 8
pu parity N
pu stopbits 1
pu rtscts No
- Start minicom Execute the following command to connect to the ArmSoM product based on Rockchip chip. The parameter rockchip is to use the above configuration.
minicom rockchip
Q1: If the device manager does not see the device
A1: You need to install the driver of the corresponding serial port yourself
Q2: When using the debug console, there is system startup information on the screen, but you cannot use the keyboard to enter text
A2: Hardware Flow Control may be enabled by default. Turning off Hardware Flow Control should restore to normal.
4.3.4 HDMI display and mouse and keyboard
As long as it is a product with a desktop system, plug in the HDMI interface data cable to connect the screen, plug in the mouse and keyboard, enter the desktop to operate the serial port, file system, etc.
4.3.5 SSH access
SSH is pre-integrated in the official ArmSoM Linux image to facilitate remote terminal access. This guide takes ArmSoM-W3 as an example. The operations of other motherboards are similar.
4.3.5.1. Necessary preparations
- ArmSoM Internet-enabled product
- RJ45 network cable
- Host PC
- Router/switch
Connect ArmSoM-W3 to a router/switch in the same network segment as the host through a network cable.
4.3.5.2 Check the SSH service status
After ArmSoM-W3 is started, you can check the SSH service status with the following command:
sudo service ssh status
If the SSH service is abnormal or uninstalled, you can restart or reinstall it with the following command: Restart the service:
service sshd restart
Reinstall:
sudo apt-get update
sudo apt-get install ssh
4.3.5.3 Query the IP address
To view it through the command line, you can use the serial port/adb/directly connect to the HDMI, and enter the following command in the terminal to view the IP address
ip a
The IP address in the same network segment as the host is the IP address required for SSH connection. For example, in the following output, 192.168.10.59 is the IP address we need:
armsom@armsom-w3:~$ ip a
1: lo: <LOOPBACK,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 65536 qdisc noqueue state UNKNOWN group default qlen 1000 link/loopback 00:00:00:00:00:00 brd 00:00:00:00:00:00 inet 127.0.0.1/8 scope host lo valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever 2: enP4p65s0: <BROADCAST,MULTICAST,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 1500 qdisc mq state UP group default qlen 1000 link/ether 8a:e5:4e:f3:ea:5a brd ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff permaddr 2a:ab:ea:32:56:cc inet 192.168.10.59/24 brd 192.168.10.255 scope global dynamic noprefixroute enP4p65s0
valid_lft 85861sec preferred_lft 85861sec
Use Angryip to find the IP address of the product
When you cannot directly operate the motherboard to obtain the IP address in a screenless or remote situation, you can use this method to query the IP address.
First, the host PC needs to download Angryip, and then make sure that the host PC and the ArmSoM product are in the same LAN.
Open Angryip and select the IP range, which is between 192.168.10.0 - 192.168.10.255 (select the network segment where the host and motherboard are located). Click Start, as shown in the figure.
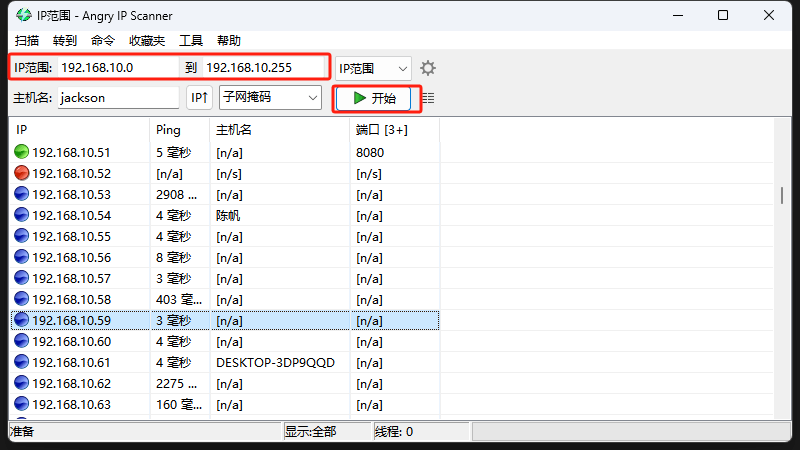
Ctrl + F to search for the keywords armsom and find the IP address.
4.3.5.4 Connection
Open the host terminal and use the ping command to check whether they are in the same network segment:
ping the IP address of the ArmSoM product
The ping result should be normal if it is connected.
- SSH login to ArmSoM-W3
ssh name@armsom-w3 IP address
For example: ssh armsom@192.168.0.1
- If the local domain name is supported, the following command can be used instead of scanning the IP address of ArmSoM-W3.
ping armsom-w3.local
ssh armsom@armsom-w3.local
Once connected correctly, the terminal will switch to the remote terminal of ArmSoM-W3, as shown below:
Linux armsom-w3 5.10.160 #1 SMP Wed Nov 8 15:45:13 CST 2023 aarch64
The programs included with the Debian GNU/Linux system are free software;
the exact distribution terms for each program are described in the
individual files in /usr/share/doc/*/copyright.
Debian GNU/Linux comes with ABSOLUTELY NO WARRANTY, to the extent
permitted by applicable law.
armsom@armsom-w3:~$ ip a
1: lo: <LOOPBACK,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 65536 qdisc noqueue state UNKNOWN group default qlen 1000
link/loopback 00:00:00:00:00:00 brd 00:00:00:00:00:00
inet 127.0.0.1/8 scope host lo
valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever
2: enP4p65s0: <BROADCAST,MULTICAST,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 1500 qdisc mq state UP group default qlen 1000
link/ether 8a:e5:4e:f3:ea:5a brd ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff permaddr 2a:ab:ea:32:56:cc
inet 192.168.10.59/24 brd 192.168.10.255 scope global dynamic noprefixroute enP4p65s0
valid_lft 85861sec preferred_lft 85861sec
Now you can operate the terminal.
4.4 Login username and password
| User | Username | Password |
|---|---|---|
| Ordinary user | armsom | armsom |
First enter the username (case sensitive) and then enter the password (there will be no text prompt when entering the password, so you need to pay attention to the Chinese input method and capitalization)
If the username and password are correct, you will enter the terminal
To modify the username, you can use the usermod command, and to modify the password, you can use the passwd command.