6. RKLLM
6.1 Introduction to RKLLM
The RKLLM software stack can help users quickly deploy AI models on Rockchip chips. The overall framework is as follows:
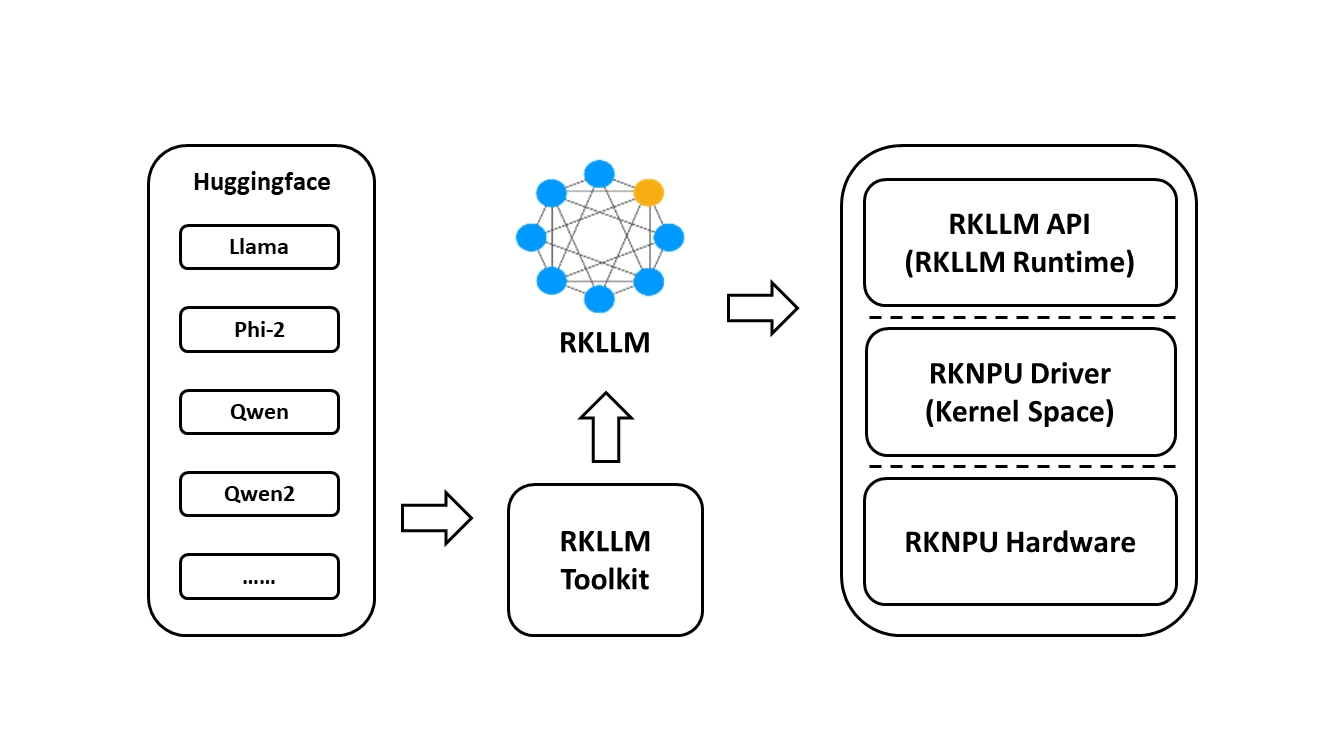
6.1.1 Introduction to RKLLM toolchain
6.1.1.1 Introduction to RKLLM-Toolkit
RKLLM-Toolkit is a development kit that provides users with the ability to quantize and convert large language models on a computer. The Python interface provided by the tool can be used to easily complete the following functions:
- Model conversion: Supports conversion of large language models (LLM) in Hugging Face format to RKLLM models. Currently supported models include LLaMA, Qwen/Qwen2, Phi2, etc. The converted RKLLM model can be loaded and used on the Rockchip NPU platform.
- Quantization function: supports quantizing floating-point models to fixed-point models. Currently supported quantization types include w4a16 and w8a8.
6.1.1.2 Introduction to RKLLM Runtime Function
RKLLM Runtime is mainly responsible for loading the RKLLM model converted by RKLLM-Toolkit, and implementing the inference of the RKLLM model on the Rockchip NPU by calling the NPU driver on the RK3576/RK3588 board. When inferring the RKLLM model, users can define the inference parameter settings of the RKLLM model, define different text generation methods, and continuously obtain the inference results of the model through pre-defined callback functions.
6.1.2 Introduction to RKLLM Development Process
The overall development steps of RKLLM are mainly divided into two parts: model conversion and board deployment and operation.
- Model conversion: In this stage, the large language model in Hugging Face format provided by the user will be converted to RKLLM format for efficient inference on the Rockchip NPU platform. This step includes:
- a. Get the original model: Get the large language model in Hugging Face format; or the large language model trained by yourself, the structure of the model saved is required to be consistent with the model structure on the Hugging Face platform.
- b. Model loading: Load the original model through the rkllm.load_huggingface() function.
- c. Model quantization configuration: Build the RKLLM model through the rkllm.build() function. During the building process, you can choose whether to perform model quantization to improve the performance of the model deployed on the hardware, and choose different optimization levels and quantization types.
- d. Model export: Export the RKLLM model to a .rkllm format file through the rkllm.export_rkllm() function for subsequent deployment.
- Board deployment and operation: This stage covers the actual deployment and operation of the model. It usually includes the following steps:
- a. Model initialization: Load the RKLLM model to the Rockchip NPU platform, set the corresponding model parameters to define the required text generation method, and define the callback function for receiving real-time inference results in advance to prepare for inference.
- b. Model inference: Perform inference operations, pass input data to the model and run model inference. Users can continuously obtain inference results through pre-defined callback functions.
- c. Model release: After completing the inference process, release model resources so that other tasks can continue to use the computing resources of the NPU. These two steps constitute the complete RKLLM development process, ensuring that large language models can be successfully converted, debugged, and ultimately deployed efficiently on the Rockchip NPU.
6.1.3 Applicable hardware platforms
The hardware platforms applicable to this document mainly include: RK3576, RK3588
6.2 Development environment preparation
The released RKLLM toolchain compressed file includes the whl installation package of RKLLM-Toolkit, the relevant files of RKLLM Runtime library and reference sample code. The specific folder structure is as follows:
doc
└──Rockchip_RKLLM_SDK_CN.pdf # RKLLM SDK description document
rkllm-runtime
├──example
│ └── src
│ └── main.cpp
│ └── build-android.sh
│ └── build-linux.sh
│ └── CMakeLists.txt
│ └── Readme.md
├──runtime
│ └── Android
│ └── librkllm_api
│ └──arm64-v8a
│ └── librkllmrt.so # RKLLM Runtime library
│ └──include
│ └── rkllm.h # Runtime header file
│ └── Linux
│ └── librkllm_api
│ └──aarch64
│ └── librkllmrt.so
│ └──include
│ └── rkllm.h
rkllm-toolkit
├──examples
│ └── huggingface
│ └── test.py
├──packages
│ └── md5sum.txt
│ └── rkllm_toolkit-1.0.0-cp38-cp38-linux_x86_64.whl
rknpu-driver
└──rknpu_driver_0.9.6_20240322.tar.bz2
This chapter will introduce the installation of RKLLM-Toolkit and RKLLM Runtime in detail.
RKLLM-Toolkit environment is deployed on x86 server
6.2.1 RKLLM-Toolkit Installation
This section mainly describes how to install RKLLM-Toolkit through pip. Users can refer to the following specific process instructions to complete the installation of RKLLM-Toolkit tool chain.
6.2.1.1 Installation through pip
Install miniforge3 tool
To prevent the system from requiring multiple versions of Python environments, it is recommended to use miniforge3 to manage Python environments. Check whether miniforge3 and conda version information are installed. If they are already installed, you can skip this step.
conda -V
# If the prompt conda: command not found indicates that conda is not installed
# Prompt, for example, version conda 23.9.0
Download the miniconda3 installation package
wget -c https://mirrors.bfsu.edu.cn/anaconda/miniconda/Miniconda3-latest-Linux-x86_64.sh
Install miniconda3
chmod 777 Miniconda3-latest-Linux-x86_64.sh
bash Miniconda3-latest-Linux-x86_64.sh
Create RKLLM-Toolkit Conda environment
Enter Conda base environment
source ~/miniconda3/bin/activate # miniconda3 is the installation directory
# (base) xxx@xxx-pc:~$
Create a Conda environment named RKLLM Toolkit for Python 3.8 version
conda create -n RKLLM-Toolkit python=3.8
Enter RKLLM-Toolkit Conda environment
conda activate RKLLM-Toolkit
# (RKLLM-Toolkit) xxx@xxx-pc:~$
6.2.1.2 Install RKLLM-Toolkit
Use pip to directly install the provided toolchain whl package in the RKLLM-Toolkit Conda environment. During the installation process, the installation tool will automatically download the related dependency packages required by the RKLLM-Toolkit tool.
pip3 install rkllm_toolkit-1.0.0-cp38-cp38-linux_x86_64.whl
If there is no error when executing the following command, the installation is successful.
python
from rkllm.api import RKLLM
6.2.2 Use of RKLLM Runtime Library
The public RKLLM toolchain file includes all the files containing RKLLM Runtime:
- lib/librkllmrt.so: RKLLM Runtime library for RK3576/RK3588 board to call for RKLLM model deployment reasoning;
- include/rkllm_api.h: The header file corresponding to the librkllmrt.so function library, which contains the description of the relevant structure and function definition; When building the deployment reasoning code for the RK3576/RK3588 board through the RKLLM toolchain, it is necessary to pay attention to the linking of the above header files and function libraries to ensure the correctness of the compilation. When the code is actually running on the RK3576/RK3588 board, it is also necessary to ensure that the above function library files are successfully pushed to the board, and complete the declaration of the function library through the following environment variable settings:
ulimit -Sn 50000
export LD_LIBRARY_PATH=./lib
./llm_demo qwen.rkllm
6.2.3 Compilation requirements for RKLLM Runtime
When using RKLLM Runtime, you need to pay attention to the version of the gcc compiler. It is recommended to use the cross-compilation tool gcc-arm-10.2-2020.11-x86_64-aarch64-none-linux-gnu; the specific download path is: GCC_10.2 cross-compilation tool download address.
Please note that cross-compilation tools are often backward compatible but not upward compatible, so do not use versions below 10.2.
If you choose to use the Android platform, you need to compile Android executable files. It is recommended to use the Android NDK tool for cross-compilation. The download path is: Android_NDK cross-compilation tool download address. It is recommended to use the r18b version.
For specific compilation methods, you can also refer to example/build_demo.sh in the RKLLM-Toolkit tool chain file.
6.2.4 Chip Kernel Update
Since the currently publicly available firmware kernel driver version does not support the RKLLM tool, the kernel needs to be updated. The rknpu driver package supports two main kernel versions: kernel - 5.10 and kernel - 6.1. For kernel - 5.10, the recommended specific version number is 5.10.198, and the repo is GitHub - rockchip - linux/kernel at develop - 5.10. For kernel - 6.1, the recommended specific version number is 6.1.57. You can confirm the specific version number in the Makefile at the root directory of the kernel. The update steps are as follows:
a. Download the compressed package rknpu_driver_0.9.6_20240322.tar.bz2.
b. Unzip the compressed package and overwrite the rknpu driver code in it to the current kernel code directory.
c. Re - compile the kernel.
d. Burn the newly compiled kernel into the device.
6.3 DeepSeek - R1 RK35XX Deployment
- Download the DeepSeek - R1 - 1.5B HunggingFace model
- Create a new directory and download all the files here. deepseek-ai/DeepSeek-R1-Distill-Qwen-1.5B at main
6.3.2. Model Transformation
Firstly, we need to create the rkllm model with data_quantit.json for quantization. We will use the fp16 model to generate the results as quantization calibration data. Secondly, run the following code to generate data_quant. json and export the rkllm model.
cd rknn-llm/examples/DeepSeek-R1-Distill-Qwen-1.5B_Demo/export
python generate_data_quant.py -m /path/to/DeepSeek-R1-Distill-Qwen-1.5B
python export_rkllm.py
If it is a 3576 development board, it is necessary to modify export_rkllm. py
target_platform = "RK3576"
num_npu_core = 2
After execution, the .rkllm model file will be generated in the directory
6.3.3. C++ demonstrate
In the deploy directory, there is example code for board side inference
cd rknn-llm/examples/DeepSeek-R1-Distill-Qwen-1.5B_Demo/deploy
# for linux
./build-linux.sh
# for android
./build-android.sh
# push install dir to device
adb push install/demo_Linux_aarch64 /data
# push model file to device
adb push DeepSeek-R1-Distill-Qwen-1.5B-rk35**.rkllm /data/demo_Linux_aarch64
Before running the script, it is necessary to modify the compiler position of the development board For example:
GCC_COMPILER_PATH=~/customized_project/3576/rk3576_linux_rkr5/linux/prebuilts/gcc/linux-x86/aarch64/gcc-arm-10.3-2021.07-x86_64-aarch64-none-linux-gnu/bin/aarch64-none-linux-gnu
6.3.4. Run demonstration
Example of running a directory on the /data/demo_Linux_arch64 board
adb shell
cd /data/demo_Linux_aarch64
# export lib path
export LD_LIBRARY_PATH=./lib
taskset f0 ./llm_demo ./DeepSeek-R1-Distill-Qwen-1.5B_W8A8_RK3576.rkllm 2048 4096
- If you copy from the demo, remove the scene prompt words. DeepSeek does not need prompt words.
- Pay attention to the Chinese character encoding of the input in the terminal.
- The development board memory needs to be 8G or more, and it occupies about 70% during operation.
quote: Deploy DeepSeek - R1 and Janus - Pro
6.4 Usage Environment
- Development board: ArmSoM-Sige7 / ArmSoM-Sige5 / ArmSoM-CM5 / ArmSoM-AIM7 / ArmSoM-AIM5
- Code repository: rknn-llm
6.5 Sample Purchase
- ArmSoM independent website: https://www.armsom.org/product-page/sige7
- ArmSoM independent website: https://www.armsom.org/product-page/sige5
- ArmSoM independent website: https://www.armsom.org/product-page/cm5
- ArmSoM AliExpress official store: https://www.aliexpress.com/store/1102800175
- ArmSoM Taobao official store: https://item.taobao.com/item.htm?id=757023687970
- For OEM & ODM, please contact: sales@armsom.org