7. Introduction to Rockchip boot
First, let's make it clear that there are many boot stages when we boot a Linux system;
Then we need to know how to package the firmware and where to store it;
Finally, we will explain how to write to different media and boot from there
Here is the Rockchip pre-release rkbian, which may be mentioned later
https://github.com/rockchip-linux/rkbin
7.1 Boot process
This chapter introduces the general boot process of Rockchip processors, including details on which images can be used as boot paths on the Rockchip platform.
Use U-Boot TPL/SPL from upsream or rockhip U-Boot, complete source code.
Use Rockchip idbLoader, which is composed of Rockchip ddr init bin file and miniloader bin file in Rockchip rkbin project
+--------+----------------+----------+-------------+---------+
|Boot phase | Terminology | Program name | RK image name | Image location |
+--------+----------------+----------+-------------+---------+
| 1 | Primary | ROM code | BootRom | |
| | Program | | | |
| | Loader | | | |
| | | | | |
| 2 | Secondary | U-Boot |idbloader.img| 0x40 | pre-loader
| | Program | TPL/SPL | | |
| | Loader (SPL) | | | |
| | | | | |
| 3 | - | U-Boot | u-boot.itb | 0x4000 | including u-boot and atf
| | | | uboot.img | | only used with miniloader
| | | | | | |
| | | ATF/TEE | trust.img | 0x6000 | only used with miniloader
| | | | | | |
| 4 | - | kernel | boot.img | 0x8000 |
| | | | | | |
| 5 | - | rootfs | rootfs.img | 0x40000 |
+--------+----------------+----------+-------------+---------+
When we talk about booting from eMMC/SD/U-Disk/net, they are different concepts
- Stage 1 is always in the boot ROM, which loads stage 2 and may load stage 3 (when SPL_BACK_TO_BROM option is enabled).
- Boot from SPI flash means stage 2 and 3 (SPL and U-Boot only) firmware in SPI flash and stage 4/5 firmware elsewhere;
- Boot from eMMC means all firmware in eMMC (including stage 2, 3, 4, 5);
- Boot from SD card means all firmware in SD card (including stage 2, 3, 4, 5);
- Boot from USB disk means stage 4 and 5 (excluding SPL and U-Boot) firmware in disk, optionally only stage 5;
- Boot from net/tftp means stage 4 and 5 firmware on network (excluding SPL and U-Boot);
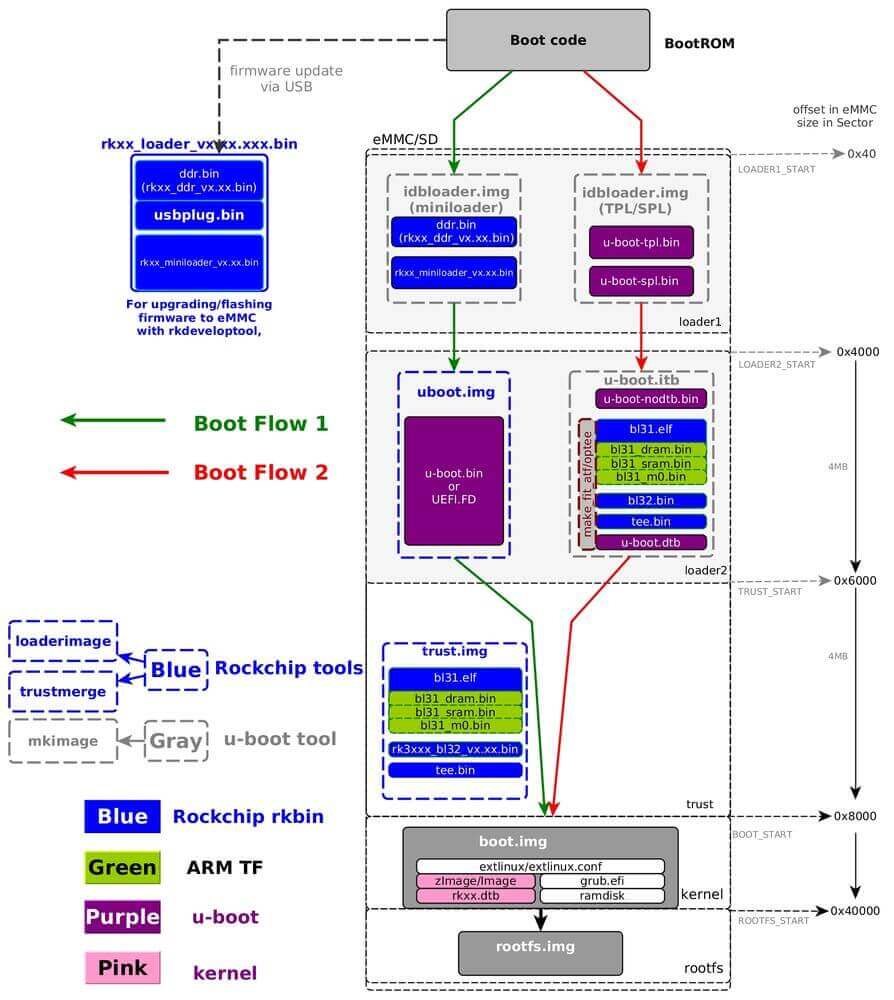
Boot flow 1 is a typical Rockchip boot flow with Rockchip miniloader; Boot flow 2 is suitable for most SoCs, where U-Boot TPL is used for ddr Initialize, SPL for trust (ATF/OP-TEE) load and run to next stage;
Note 1. If loader1 has more than 1 stage, the program will return to bootrom, and load bootrom and run to next stage. For example. If loader1 is tpl and spl, bootrom will first run to tpl, tpl init ddr and return to bootrom, bootrom load and run to spl. Note 2. If trust is enabled, loader1 needs to load both trust and u-boot, then run trust in secure mode (EL3 in armv8), trust initializes and runs U-Boot in non-secure mode (EL2 in armv8). Note 3: For trust (in trust.img or u-boot.itb), armv7 only has one tee.bin, armv8 has options for bl31.elf and bl32. Note 4. The content in boot.img can be the zImage and its dtb under Linux, or you can choose grub.efi, or AOSP boot.img, ramdisk is optional;
7.2 Packaging options
After we understand the boot,
Here is the packaging list before stage 2 ~ 4:
With source code:
From U-Boot: u-boot-spl.bin, u-boot.bin (may use u-boot-nodtb.bin and u-boot.dtb instead)
From kernel: kernel Image/zImage file, kernel dtb,
From ATF (ARM Trusted firmware): bl31.elf Binaries provided by Rockchip:
ddr, usbplug, miniloader, bl31/op-tee, (all chips with 'rkxx_' and '_x.xx.bin' suffix)
We provide two different bootloader methods for different solutions, and the steps and request files are completely different. But not all platforms support both bootloader methods. Here are the types of images packaged from these files:
todo